 by Scott Martindale
by Scott Martindale
President & CEO, Sabrient Systems LLC
The New York Fed’s Global Supply Chain Pressure Index (GSCPI) for November was released today, and although it rose more than expected (likely due to disruptions from heightened global hostilities), it still suggests inflation will continue its gradual retreat, with a reading near the long-run average. But let me start by talking about October’s inflation indicators. Last week, the headline reading for Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) for October came in at 3.0% YoY, helped quite a bit by the fall in oil and gasoline prices (note: the US is producing an all-time high of 13.2 million barrels/day of crude oil). Core PCE, which is the Federal Reserve's preferred inflation metric, came in at 3.46% year-over-year. However, the month-over-month number for October versus September, which better reflects today's inflation trends and the lag effects of higher interest rates, came in at 0.16%, which annualizes to 1.98%. Keep in mind, the Fed's inflation target is 2.0%. But monthly data can be choppy, so looking at the rolling 3-month average, it annualizes to 2.37%.
Earlier reports had shown October PPI at 1.3% YoY and CPI at 3.2%, with core PPI (excluding food & energy) was 2.4% YoY, and core CPI was 4.0%. All of this was presaged by the GSCPI, which measures the number of standard deviations from the historical average value (aka Z-score) and generally foreshadows movements in inflation metrics. It plummeted from a December 2021 all-time high of +4.31 down to the October reading of -1.74—its lowest level ever. However, that ultra-low October reading has been revised to -0.39 due to “a change in exchange rate weighting methodology,” according to the New York Fed. Nevertheless, the writing was on the wall for last week’s favorable PCE report. The chart below illustrates the correlation between GSCPI, PPI, and CPI.
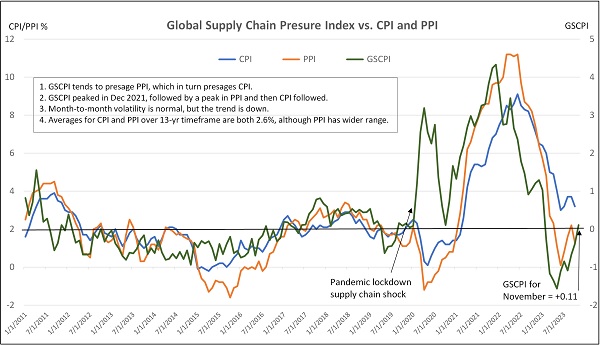
So, what to expect for November inflation? Well, as shown in the chart, GSCPI for November just came in today at 0.11. Although rising from its ultra-low levels, it still remains at the long-run average, and the chart illustrates that volatility is to be expected. All in all, I think it still bodes well for the next week’s CPI/PPI readings as supply chains continue to heal and diversify (albeit with occasional hiccups like we see today from heightened global hostilities), especially when you also consider that the consumer has become stretched with rising household debt and falling growth in job openings and wages, money supply growth is stagnant, and budget hawks are increasingly flexing their fiscal muscles in Congress. Thus, I believe the probability of a resurgence in either inflation or fiscal expansion is quite low.
Furthermore, although the second estimate for Q3 GDP was ultra-strong (the highest in 2 years), revised up to 5.2% annual rate (from previous 4.9%), the boost came from state and federal government spending, which was revised up to 5.5% from the prior estimate of 4.6% (i.e., more unsustainable deficit spending and issuance of Treasuries paying high coupons, mostly from an 8.2% increase in defense spending), while personal consumption was revised down to 3.6% from 4.0%. This tells me the “robust” GDP number was something of an illusion.
Indeed, looking ahead, the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow forecasts only 1.3% GDP growth and 1.9% PCE growth for Q4 (as of 12/6). Moreover, the good folks at Real Investment Advice observed that Gross Domestic Income (GDI) for Q3 was reported at only +1.5%, displaying the widest gap below GDP in 50 years. (Note: GDP measures the value of goods and services produced, including consumption expenditures, investments and exports, while GDI measures incomes earned and costs incurred in production of GDP, including wages, profits, and taxes.) Also, last week’s Fed Beige Book showed that two-thirds of Fed districts reported slower economic activity over the prior six weeks, and the ISM Manufacturing Index came in at an anemic 46.7, showing continued contraction for the 15th straight month.
So, this all seems to be more “bad news is good news” when it comes to Fed policy moves, and investors will be eagerly watching Friday’s jobs report followed by next week’s CPI, PPI, and FOMC policy announcement. Stocks have been taking a healthy breather and consolidation in anticipation of it all, but so far, no major pullback. This year seems to be following the playbook of what economist Ed Yardeni has characterized as a series of “rolling recessions” (among sectors) and an “Immaculate Disinflation,” i.e., moderating inflation without a harsh recession or massive layoffs. As an aside, I have opined many times that it is ridiculous that we constantly find ourselves awaiting the edict of this unelected board of “wise elders” to decide our economic fate. Why can’t they take emergency measures only when absolutely necessary to avert economic cataclysm, and then once the crisis has passed, those emergency measures are quickly withdrawn so that the free market can get back to doing its productive, creative, wonderful thing? One can dream.
Regardless, in my view, the Fed is likely done with rate hikes and preparing for its eventual pivot to rate cuts—which I think will come sooner than most expect, likely before the end of H1 2024. Why? Because if inflation maintains its gradual downtrend while the Fed holds its overnight borrowing rate steady, the real (inflation-adjusted) rate keeps rising, i.e., de facto tightening. Indeed, Fed funds futures are projecting 98% chance for no rate change next week, and for 2024, 62% chance for at least one 25-bp rate cut by March, 97% for at least one 25-bp cut by June, and 89% chance of a full 1.0% in total rate cuts by December 2024, which would put the fed funds rate below 4.5%.
Accordingly, after kissing the 5% handle, the 10-year Treasury yield has fallen precipitously to below 4.2%—a level last seen at the end of August. So, I encourage and expect the FOMC to follow the message of the bond market and begin cutting the fed funds rate back towards the neutral rate, which I think is around 2.5-3.0% nominal (i.e., 2% target inflation plus 0.5-1.0% r-star), and hand back control of the economy to the free market. As of now, the Fed is on the verge of crushing the housing market…and by extension the broader economy. In addition, it must ensure money supply resumes a modest growth rate (albeit slowly), not continue to shrink or stagnate.
To be sure, the safe steadiness of bond yields was disrupted this year. After rising much faster than anyone anticipated, interest rates have fallen much faster than expected, especially considering that the Fed hasn’t made any dovish policy changes. Nevertheless, if rates are going to generally meander lower, investors might be expected to lock in sustainable yield with capital appreciation potential through longer-duration securities, including long-term bonds, “bond proxies” like dividend-paying equities (e.g., utilities, staples, and REITs), and growth stocks (like high-quality technology companies).
I also like oil, gold and uranium stocks, as well as gold, silver, and cryptocurrency as stores of value in an uncertain macro climate. Notably, gold is challenging its highs of the past few years as global investors and central banks are both hedging and/or speculating on a weaker dollar, falling real interest rates, rising geopolitical tensions, and potential financial crisis, and the World Gold Council reported robust demand among central banks, which purchased a record 800 tons during the first three quarters of the year. Similarly, Bitcoin is catching a bid on speculation of broader investor access (through spot-price ETFs) and dollar debasement (if debt and deficit spending continue to spiral).
Keep in mind that, when valuations get lofty within a given asset class, volatility and performance/valuation dispersion among stocks often increases while correlations decrease. For stocks, active selection strategies that can exploit the dispersion to identify under-the-radar and undervalued companies primed for explosive growth become more appealing versus passive index investing. Sabrient’s actively selected portfolios include the Q4 2023 Baker’s Dozen (launched on 10/20), Small Cap Growth 40 (launched on 11/3), and Sabrient Dividend 46 (just launched on 11/29, and today offers a 4.7% dividend yield).
In today’s post, I further discuss inflation, the US dollar, Fed monetary policy implications, and relative performance of asset classes. I also discuss Sabrient’s latest fundamentals based SectorCast quantitative rankings of the ten U.S. business sectors (which is topped by Technology and Industrials), current positioning of our sector rotation model (which turned bullish in early November and remains so), and some actionable ETF trading ideas.
Click here to continue reading my full commentary … or if you prefer, here is a link to this post in printable PDF format (as some of my readers have requested).